LSSTComCam: The LSST Commissioning Camera¶
Citation: SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory & NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory, The LSST Commissioning Camera (2024)  https://doi.org/10.71929/rubin/2561361 [
https://doi.org/10.71929/rubin/2561361 [BibTeX]
The LSST Commissioning Camera (LSSTComCam) was mounted on the Simonyi Survey Telescope in August 2022 and observed for seven weeks in late 2024 until it was removed from the telescope in December 2024. It is a smaller, fully functional version of LSSTCam, with only the central raft of nine 4k x 4k CCDs (all ITL sensors) and comprising 144 megapixels. Every CCD has 16 amplifiers, each reading 1 million pixels. LSSTComCam was designed to enable end-to-end testing of the observatory’s systems, including data acquisition, image processing, and observatory operations. LSSTComCam is also referred to as the engineering test camera or, informally, as ComCam.
Focal plane¶
LSSTComCam consists of only a single “raft” of 9 CCDs (charge-coupled device, also called a sensor, detector, or chip). Each CCD is 4k x 4k pixels (4000 by 4000 pixels), for a total of 144 Mpix. For comparison, LSSTCam has 21 rafts, and 189 of the same CCDs. All of LSSTComCam’s CCDs are from ITL, one of the same two vendors that supplied the LSSTCam detectors (ITL and e2v).
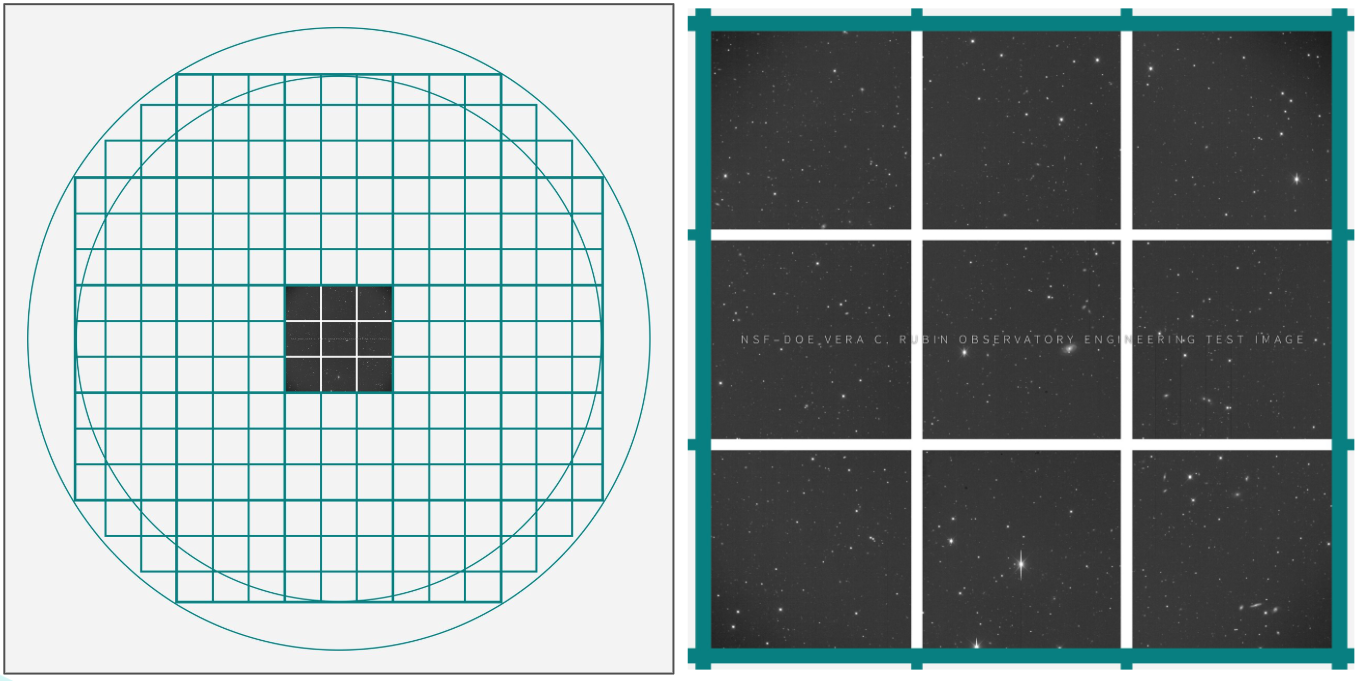
Figure 1: The LSSTComCam has only 9 CCDs compared to LSSTCam’s 189 CCDs.¶
Filters¶
LSSTComCam uses the same ugrizy filters as LSSTCam. LSSTComCam’s filter exchanger can only hold three physical filters at a time (compared to 5 for LSSTCam).
Key numbers¶
CCDs: 9
pixels: 144 Mpix
platescale: 0.2 arcsec / pixel
field of view: 40 x 40 arcminutes
read noise: 6.21 electrons (ITL sensors)
gain: 1.68 electrons / ADU (ITL sensors)
Visit Rubin Observatory’s Key Numbers page, and the page for LSSTCam, for more key numbers.
Known issues¶
LSSTComCam was the instrument used to facilitate early system integration for the Rubin Observatory. It was not, itself, commissioned. The image quality achieved during the LSSTComCam on-sky campaign, and of the data in DP1, is not necessarily indicative of the image quality that Rubin Observatory expects to achieve with LSSTCam.
Citing LSSTComCam¶
Use of the correct formal citation strings and keywords ensures that all uses of data from LSSTComCam can be found using community tools.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.71929/rubin/2561361 (refers to this document)
Use this DOI when referring to the instrument specifically; otherwise a dataset DOI may be more appropriate (see the documentation for the specific data you are using).
IVOA ObsCore keywords:
facility_name=Rubin:Simonyi,instrument_name=LSSTComCamAAS facility keyword:
Rubin:Simonyior, for specificity,Rubin:Simonyi (LSSTComCam)Minor Planet Center observatory code:
X05
References¶
Additional information is available via:
Rubin commissioning camera: integration, functional testing, and lab performance, Stalder et al. (2020; SPIE, doi:10.1117/12.2561132)
Rubin Observatory Commissioning Camera: summit integration, Stalder et al. (2022; SPIE, doi:10.1117/12.2630184)
The LSST commissioning camera status and progress, Howard et al. (2018; SPIE, doi:10.1117/12.2312684)
An interim report on the ComCam on-sky campaign, Vera C. Rubin Observatory (2025; Commissioning Technical Note SITCOMTN-149)

This material is based upon work supported in part by the National Science Foundation through Cooperative Agreement AST-1258333 and Cooperative Support Agreement AST-1202910 managed by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), and the Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-76SF00515 with the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory managed by Stanford University. Additional Rubin Observatory funding comes from private donations, grants to universities, and in-kind support from LSST-DA Institutional Members.